10 Common Knee Injuries and Diseases
Ligament tears, primarily of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), are commonly the season ending injuries we hear about in sports. Although male athletes make the headlines, women experience ACL tears 7-8 times more frequently than men due to hormonal and anatomical reasons.
The knee has 2 collateral (parallel) ligaments and 2 cruciate (crossing) ligaments. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) provide support to the knee by limiting the sideways motion of the joint. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) stabilize the knee by limiting the rotation and the forward and backward movement of the joint.
Of the 2 collateral ligaments, the MCL is the one that is injured most often. This injury is often a result of a blow to the outer side of the knee.
Of the 2 cruciate ligaments, the ACL is the one that is injured most often. This injury occurs when the knee is locked with the foot planted and the knee is twisted quickly. Athletes required to make sudden directional changes or to slow down quickly and those in contact sports are at high risk for ACL tears, especially if they are wearing cleats or skis.
Minor tears may go unnoticed immediately and will appear a few hours later with pain and swelling. More serious ACL tears are accompanied by severe pain and often a popping sound. The knee may feel as though something has snapped and walking or bending the knee is usually impossible.
Administering ice and compression immediately will help reduce pain and swelling. Treatment differs depending on the degree of instability and the patient's activity level. Many ligament injuries heal with rest and Circulation Boost (Circulatory Boost) to greatly speed the healing rate of the injured soft tissue. Circulatory Boost is exactly what the Knee TShellz Wraps® is made for.
Once your knee has improved somewhat, it is recommended that you build muscle strength around the knee with gentle stretching under the guidance of a physical therapist or physician to complete your return to normal and help prevent re-injury in the knee. If an injured ligament does not strengthen appropriately or an athlete continues to experience the knee giving way, arthroscopic surgery and ligament reconstruction may be necessary. Read more about information on ligament tears here.
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that works as a cushion between the femur and the tibia. Tearing of the meniscus occurs when the knee is twisted forcibly while under weight. As the body ages, cartilage deteriorates - this makes knee joints more susceptible to meniscal tears with minor movement. When the meniscus is torn, it starts to move abnormally inside the joint and it may become caught between the tibia and femur.
Those suffering from a meniscal tear commonly experience swelling, pain and difficulty moving the knee.
A minor tear in the meniscus may only require rest, a change in activity, and strengthening exercises to support the joint. Unfortunately, meniscal tears can be difficult to heal because blood supply is often limited to the outside edge of the meniscus cartilage. Circulation Boost will help prevent scar tissue accumulation and speed up healing by increasing the flow of blood and nutrients to the area. In the case of a large or complex tear or if disabling symptoms remain after 2-3 months, arthroscopic surgery may be recommended.
More information on meniscus function and tears.
Patellar Chondromalacia occurs when the cartilage enabling the femur and kneecap to glide smoothly over one another becomes damaged. This damage is caused by regular wear and tear or by repetitive trauma due to the knee muscles weakening and the patella (kneecap) becoming misaligned. Patellar Chondromalacia is very common in runners and is often termed as 'Runners Knee'.
Patellar Chondromalacia patients complain of tenderness under or around the kneecap and the pain often increases when using stairs or getting out of a chair. A grinding feeling may also occur when trying to straighten the knee.
When the injury becomes inflamed, icing is recommended and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, particularly the inner quadriceps is the best treatment to realign the patella. To prevent further damage to the cartilage, minimize impact exercises until the muscle strength increases.
More information on Patellar Chondromalacia.
4. Bursitis of the Knee
(Prepatellar Bursitis and Pes Anserine Bursitis)
Bursitis occurs when the bursae swell from chronic irritation, inflammation and the accumulation of excess fluid within the bursa sacs. This is commonly caused by frequent kneeling and is referred to as "housemaid's knee" as it is often suffered by people whose work requires kneeling for extended periods of time.
Symptoms include knee pain and limited motion, along with swelling and redness over the kneecap. When walking, sufferers experience extreme pain and stiffness that worsens when using stairs. A patient may also experience a fever if the bursae become infected.
When inflammation and pain occur, it is recommended that any aggravating activity be discontinued. However, even daily activities can inflame the tender sacs and cause healing time to be extended. RICE will help to ease the symptoms and promote healing. In severe cases, draining the bursae may be necessary and if fluid accumulation continues, removing the bursa may be the consequence. Follow this link for more information about bursitis (aidmybursa.com).
A fracture of the patella, can occur from an impact on the kneecap; such as in the case of a car accident, a fall or contact while playing a sport.
A fractured patella causes pain and tenderness, swelling, a limited range of motion and the inability to walk. Symptoms may also include muscle spasms and grating of bone if fragments are loose in the joint.
If the fractured bones are lined up, surgery is not necessary and a leg cast is used to immobilize the leg allowing the bones to heal. If the bones are not aligned, surgery is required and the fractured ends are set and held in place with pins and wires.
The patellar tendon joins the kneecap to the shin bone and works as part of the extensor mechanism allowing the knee to straighten out. Patellar tendonitis is an injury caused by overuse or recurring trauma to the tendon and is often seen in athletes of jumping sports like basketball or volleyball.
Sufferers experience pain and swelling at the front of the knee along with a limited range of motion. The pain often becomes more severe with jumping or kneeling.
Treatment begins with resting the knee and avoiding the symptom causing activity until symptoms settle. Cold compression and anti-inflammatory medication will assist in controlling the inflammation, decreasing swelling and managing pain. Once the tendon is no longer inflamed, physical therapy, hamstring stretching and limiting high impact activities is recommended.
More information about patellar tendonitis.
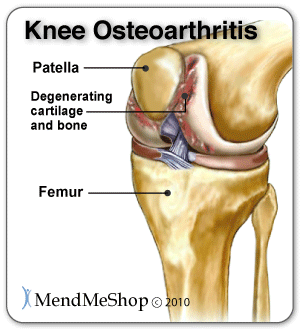
Osteoarthritis is caused by the cartilage in the knee deteriorating with wear and tear or because of trauma to the joint, ultimately leaving only bare bone. It is the most common type of knee arthritis and is also called degenerative joint disease or wear-and-tear arthritis. The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age and for people who are genetically predisposed to the disease, are overweight or have suffered knee trauma chances are even greater.
Although osteoarthritis worsens with time, sufferers experience periods of flare-ups and remission. Symptoms include increased pain with use throughout the day, joint stiffness, swelling, and tenderness. Patients often experience grinding, clicking, locking or feelings that the knee may give out. Movement of the joint can be limited and deformity may occur over time as bones become damaged.
Pain may be managed and damage minimized by decreasing the burden on the knee joint with weight loss or use of a walking aid. Low-impact and aquatic exercises and physical therapy will strengthen the muscles to support the knee joint.
Ice packs, compression wraps, anti-inflammatory medications, and certain types of injections can reduce pain and inflammation. A recent study has called into question the benefit of arthroscopic surgery and you should discuss your options with a physician before making any decisions about surgery. If osteoarthritis pain cannot be managed by these methods, surgical options will most likely be considered; knee arthroscopy, tibial osteotomy or knee replacement surgery, depending on your injury.
More information on knee osteoarthritis.
Osgood-Schlatter ("oz-good shlot-ter"") is a disease experience by adolescents, usually athletes, during a period of rapid growth. It occurs when the patellar and/or tendon pulls away from the tibia and becomes inflamed. This inflammation is a result of excess strain on the tendon due to muscles and bones growing at varying rates.
Osgood-Schlatter Disease causes swelling and pain below the knee, just above the tibia. The pain increases with exercise and is relieved when the knee is at rest. It is also common to experience tightening of the muscles and limping after strenuous activity.
As the growth spurt ends, muscles and bones catch up with one another, the patellar tendon strengthens and pain and swelling subsides. In the meantime, resting the tendon is the best way to treat Osgood-Schlatter Disease. If the pain is mild some activity may be continued, but severe pain requires discontinuation of the sport. Pain medication, heating the joint before playing and icing it afterwards can control swelling and pain. It is important to not play through the pain and attend to the injury as needed or recovery time is extended.
A patellar (kneecap) dislocation occurs when one of the ligaments securing the patella to the knee, usually the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL), tears and allows the patella to fall out of its groove.
The most obvious symptom is the kneecap's ability to move freely from side to side. In addition, intense pain, swelling and the inability to walk or straighten the knee will be experienced.
Bracing the knee to allow the MPFL to heal is the first treatment option. However, this can be ineffective as it is difficult for the MPFL to heal without proper tension. If the ligament does not heal correctly, the chance of dislocation recurring is high. Surgery to repair the ligament may be necessary and should be discussed with a physician if proper healing does not occur.
Gout is a type of arthritis that is identified by a severe and rapid onset of pain. The pain is a result of an accumulation of uric acid in the knee. It is often an inherited disease but other factors contributing to gout include obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, kidney malfunctions and certain types of cancer.
Gout sufferers will experience sudden and severe pain, warmth, redness, swelling and tenderness of the knee joint. They may also suffer from kidney stones or kidney failure which causes the uric acid to enter the blood stream.
Preventing gout attacks can be achieved with weight reduction, limited alcohol consumption and adequate fluid consumption. Lowering uric-acid levels with medication or dietary modifications (i.e. limiting purine-rich foods and increased consumption of dairy products) can also reduce inflammation. When gout attacks occur, anti-inflammatory medications may be used to control the pain. Other medications available to gout sufferers include colchicines, which is used to reduce gout pain quickly, and other otc meds used to prevent future attacks. As with any medication, it is important to consult your doctor to see if the medication is right for you.
Taking measures to protect your knees and maintain healthy joints is something everyone can do to prevent knee pain. Should knee injury or disease become a part of your life, understanding your condition is the first step in determining the appropriate treatment. Get an accurate diagnosis from your physician and discuss your options. Proper treatment will allow you to resume your activities faster and safer.
Our customer service lines are open 5 days a week helping people understand our products and how they relate to soft tissue knee injuries. Simply call toll free 1-866-237-9608 to talk with one of our knowledgeable Product Advisors.
Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday.
Learn More About Knee Injuries & TreatmentsI want to learn more about post-surgery recovery. I want to learn all about common causes of knee pain. I want to learn more about TShellz Wrap® Circulatory Boost I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Treatment? I want to learn more about Knee Treatments. I want to learn more about Runners Knee. I want to learn more about Hoffas Syndrome. I want to learn more about Knee Arthritis. I want to learn more about Knee Trigger Points.
FREE SHIPPING ON ALL PRODUCTS CURRENTLY ENABLED
60 DAY TRIAL PERIOD
During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort at the location of your soft tissue injury until the pain and inflammation settle. The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results!
|