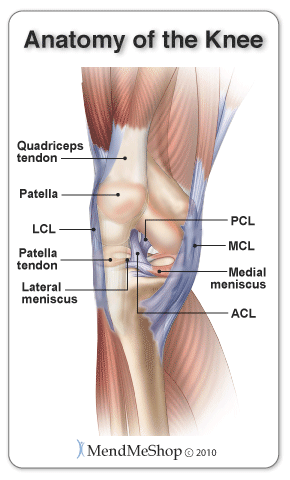
| Anatomy of the KneeKnee Tendons and LigamentsThe patellar ligament (also referred to as the patellar tendon) is located below the patella. It is approximately 4 inches long and inserts at the top of the tibia and spreads over top of the patella where it connects to the quadriceps tendon. The patella tendon is most commonly injured or inflicted with tendonitis, known as Jumper's Knee (patellar tendonitis). The upper leg muscles provide your knees with mobility (extension, flexion and rotation) and strength. The quadriceps muscles located at the front of your thigh (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius), allow you to straighten your legs and the hamstring muscles, located on the back of your thigh (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris), allow you to bend your knees. The tendon of the quadriceps runs from the quadriceps muscles, down both sides of the patella and join on either side of the tibia. This tendon is susceptible to quadriceps tendinitis. Ligaments are strong, elastic-like tissues that connect bone to bone and provide stability and protection to your knee joint by limiting the forward and backward movement of the shin bone. There are four ligaments in the knee joint that connect the femur and tibia; the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), the medial collateral ligament (MCL), and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
The knee ligament that is most frequently injured is the anterior cruciate ligament. A pivot, twist or over-extension of the knee can lead to an ACL strain or tear. Lateral Meniscus and Medial MeniscusThe menisci are crescent shaped wedges located in the knee joint at the bottom of your thigh bone and on top of the flat upper surface of your shin bone. They are made of a dense, collagen connective tissue that is tougher than articular cartilage, called fibro-cartilage. Menisci cover approximately 2/3 of your tibia surface and are thinner on the inside and thicken toward the outer peripheral. They fill the space between these bones and cushion your femur (similar to shock absorbers) so it doesn't rub against your tibia or slide off. 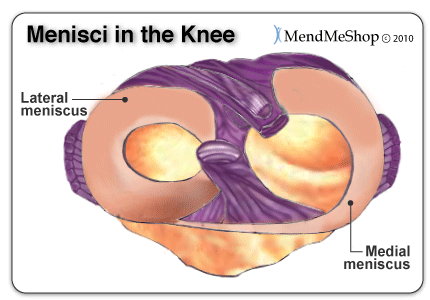 When you walk, your weight shifts from one meniscus to the other which can increase the forces on your knee by up to 2 - 4 times your body weight; when you run the forces increase up to 6 - 8 times your body weight, and are even higher when landing from a jump. The menisci help distribute the weight of your body across your knee joint, lubricate and protect the articular cartilage from damages from wear and tear, stabilize your knee when you slide and turn, and limit extreme knee flexion and extension. Due to the weight bearing and stabilizing function of the menisci they are very strong, but they are also quite prone to a meniscus tear. There are 2 menisci - the lateral meniscus (located on the outside of your knee) and the medial meniscus (located on the inside of your knee). The lateral meniscus is more of an "O" shape, and although it is slightly shorter in length, it covers a larger portion of the tibia surface. It is very mobile and is only attached to the tibia on the outside and back of your joint. It slides forwards and backwards, moving freely in the joint, absorbing up to 80% of the load applied to the outside of your knee. The lateral meniscus is less likely to be injured or torn by force, because it can move and change shape. The medial meniscus is about 3.5cm in length and more of a c-shape, resembling a wedge of an orange. It is tightly attached to the tibia and joint capsule on the back and inside of your knee. It helps the ACL and MCL stabilize your knee, absorbing up to 50% of the load applied to the inside of the knee. The medial meniscus is quite inflexible and does not move freely in the joint, therefore, it is torn more frequently than the lateral meniscus. Bursae in the Knee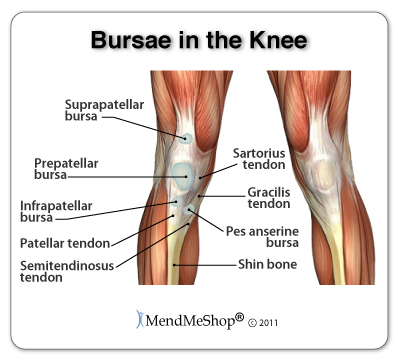 In amongst the bones, tendons, and ligaments rest bursa sacs that function as cushions to reduce friction and allow your soft tissue to slide easily and comfortably within your knee. The bursae are lined with synovial cells that secret a fluid rich in protein and collagen and act as the lubricant between areas in your knee where friction (rubbing) is greatest. There are 4 major bursae in each knee including the prepatellar bursa, supra-patellar bursa, infra-patellar bursa, and pes anserine bursa. With too much friction or pressure on the bursae, they can become irritated and inflamed - such a condition (as you likely know) is called bursitis. Prepatellar bursitis and pes anserine bursitis are the most common types of bursitis pain in the knees. Articular Cartilage and Synovial FluidArticular cartilage, also known as hyaline cartilage, is a type of slick, hard, bone-like, flexible connective tissue that covers the surface ends of the tibia and femur at your knee joint, reducing friction and allowing the bones to move easily against one another. It is generally 1/8 to 1/4 inch thick. Synovial fluid is a thick, stringy, yolk-like fluid that is secreted by the synovial tissue inside the knee capsule. It nourishes the cartilage and lubricates the knee joint. Wear and tear in the knee joint can cause the protective cartilage to begin to break down. When this occurs it is called osteoarthritis and if left untreated, it can lead to permanent cartilage loss and chronic knee pain. MendMyKnee advisors do not work on commission, so be assured you will only receive fair and objective information. Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday. Learn More About Knee Injuries & TreatmentsI want to learn more about post-surgery recovery. I want to learn all about common causes of knee pain. I want to learn more about TShellz Wrap® Circulatory Boost I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Treatment? I want to learn more about Knee Treatments. I want to learn more about Runners Knee. I want to learn more about Hoffas Syndrome. I want to learn more about Knee Arthritis. I want to learn more about Knee Trigger Points. FREE SHIPPING ON ALL PRODUCTS CURRENTLY ENABLED |
      |